January 11, 2017
Enterprise Content Management: An Overview
Information may exist in different forms, such as text documents, spreadsheets, images, XML files, web pages, video, audio, and email, or in more fixed content pieces like reports, records, and scanned images.
An Enterprise Content Management system provides order to such raw and unstructured information. It takes care of the creation, management, processing, delivery, and retention/archival of any content based on business rules. It essentially creates relationships between pieces of content, thus allowing the same content to be used in different contexts and formats.
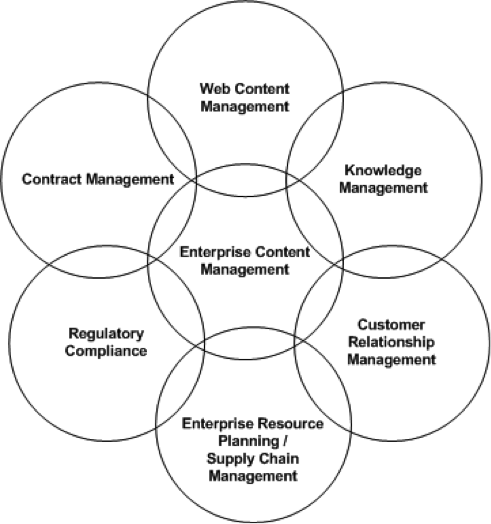
It facilitates creating categorization schema and metadata (properties) that can make searching the content simple, fast, and efficient. It enables users to process content through a business process or a lifecycle and allows publication through multiple channels; for example, the same content can be published to a web site, broadcasted as a fax, printed as a text document, and sent to handheld devices. The figure below depicts the uses of content management applications across different industries.
Building Blocks on Enterprise Content Management
Managing information is imperative to the success of a business, and a lot of that success lies in how they make it available to the right people at the right time. Everyone benefits from increased connectivity. An enterprise content management platform provides a foundation for this level of connectedness through its four building blocks:
- Pervasive content management
- Complete content lifecycle
- Creation of content management applications
- Connected applications for completing digital value chain
Pervasive Content Management
Pervasive content management is the ability to manage all content types anytime, anywhere. Any enterprise content management platform can generally store content files in all known formats and provide easy extensibility to other formats. It also provides OOTB tools to integrate with many popular content authoring tools used to capture content, like MS Word, MS Excel, MS Outlook, and Lotus Notes. The effectiveness of such a platform comes from the fact that it manages all the phases of content – from creation, to storage, versioning, delivery, archival, and disposal as per regulated laws and corporate policies.
Pervasive content management also means working effectively with other components on the infrastructure, such as the operating systems, relational database management systems, Web application servers, and enterprise applications such as ERP and CRM. An enterprise content management platform connects efficiently with these systems and provides a distributed repository so that companies can access and deploy their content any time and any place around the world.
Content Lifecycle
Any enterprise content management platform can manage content from the moment it is created to publishing the content to a corporate web site, distributing engineering specifications, or delivering invoices to customers. This is called the lifecycle of content and can be broadly classified into four major stages:
- Creating content
- Managing content
- Delivering content
- Archiving content
Content Creation
An enterprise content management platform integrates with authoring applications such as Microsoft Office products, Adobe publishing products, XML authoring tools, and CAD applications, enabling application users to add and retrieve content files directly from the content repository. The integration uses standard protocols and interfaces such as WebDAV and ODMA.
Managing Content
An enterprise content management platform provides a content repository, which is its foundation. This is a secured storage area that provides organized access to the content, regardless of the source or format. Each item in the repository is protected by powerful and flexible security that controls who can access the content and what level of access each person has. It also provides a versioning mechanism that enables the tracking and management of multiple version of the same content.
Delivering content
Delivering content is mainly handled through content applications serving the platform. Content applications may have a heterogeneous population of users – from IT personnel and developers to non-technical staff in many functional departments. The content applications provide appropriate interfaces to access content based on pre-defined security roles. Any enterprise content management platform will provide an OOTB content application that a business can use to get a head start.
Archiving Content
An enterprise CMS platform enables businesses to preserve content in a trusted, scalable, and cost-effective way. As a result, businesses can take advantage of any type of storage infrastructure they choose, including JBOD, RAID, CD and DVD jukeboxes, optical laser disks, and tape data storage, as well as sophisticated networked storage systems such as network attached storage (NAS) or storage area networks (SAN).
Creating Customized Content Applications
A CMS platform, although it provides an OOTB content application as a part of its product package, generally enables businesses to create their own content application by providing an SDK (software development kit). This development kit can be used by developers to customize/configure existing content applications or create a new one, as per the business requirements.
In general, business logic can be encapsulated in the core components and can be exposed as Web services to provide access through other applications. Web services are a natural mechanism for integrating content management across systems, such as CRM, ERP, and portals.
Completing the Digital Value Chain
The digital value chain is the integrated set of applications and processes – within the enterprise and extending to suppliers, distributors, and customers – that support the creation, management, processing, distribution, and archival of any kind of electronic content. This is achieved by connecting the existing applications with the CMS platform.
Summary
In summary, an enterprise content management platform can provide an end-to-end solution that the business can use to unite teams, content, and associated business processes. With a single platform, it can enable people to collaboratively create, manage, deliver, and archive all types of content, from documents and discussions to e-mail, Web pages, records, and rich media. Thus organizations can improve their competitive advantage by accelerating time to market, increasing customer satisfaction, and reducing operating costs.